Life Outcomes Related to Personality
Discover how personality traits predict important outcomes across individual, interpersonal, and social-institutional domains
Over the last 100 years, there has been a growing body of academic research dedicated to understanding and working towards defining personality and how differences among personalities are related to important individual, interpersonal, and social-institutional outcome constructs that impact our lives in important ways (Ozer & Benet, 2006). Large-scale replication studies have reinforced confidence in these findings (Soto, 2019). Thus far, there are over 40 outcomes which have been found by peer-reviewed research to have a valid and reliable relationship with five factor personality traits. Outcomes can be associated with one or more of the five factor traits and the relationship can be positive or negative.
100+
Years of Research
40+
Validated Outcomes
3
Outcome Domains
Outcomes Visualization
See how personality traits connect to life outcomes
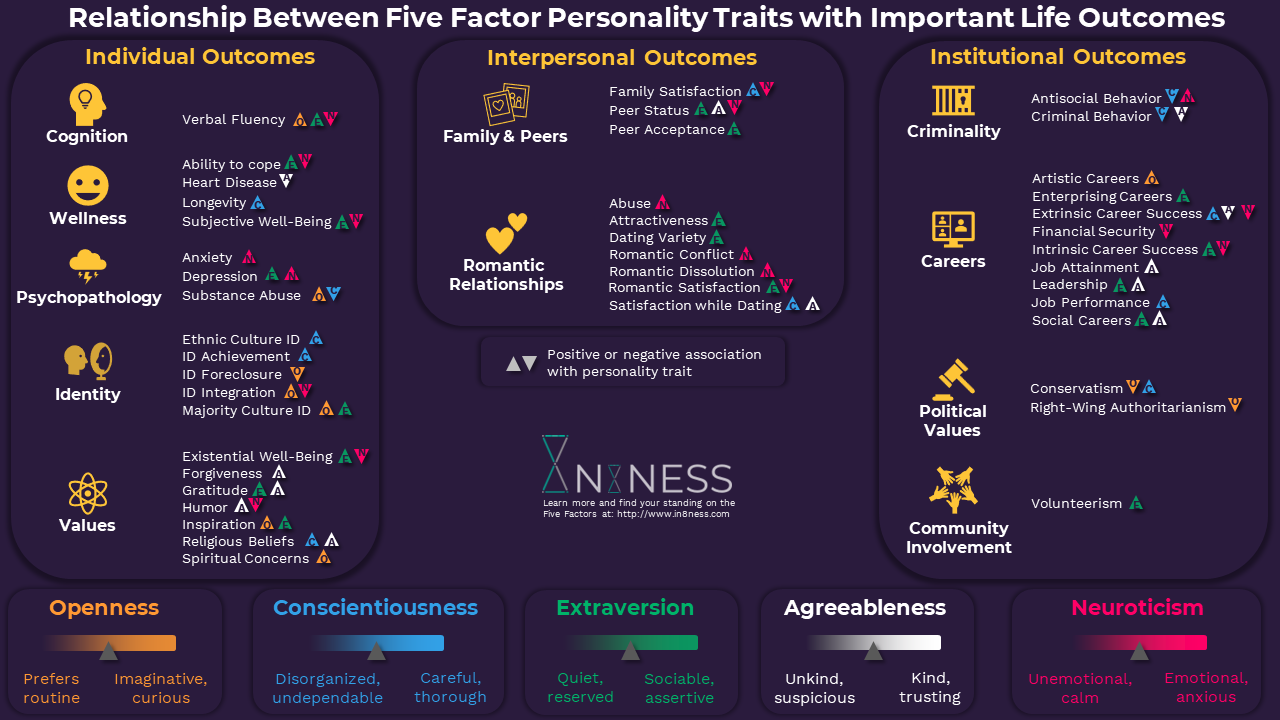
Individual Outcomes
Individual level outcomes are those that mainly have an impact to ones' self. Related outcomes include cognitive ability, happiness, physical and mental health, self-identity, and personal values.
Appreciate mellow music styles
Definition
Mellow musical styles feature romantic, slow, and quiet attributes, typically found in genres like soft rock, R&B, and adult contemporary.
Related Traits
Appreciate unpretentious music styles
Definition
Unpretentious musical styles are defined by uncomplicated, relaxing, and unaggressive attributes, often heard in country genres.
Related Traits
Coping
Definition
Coping refers to the ability to overcome a stressful situation. Strategies that are commonly used to cope include: distraction, redefinition, direct action, catharsis, acceptance, social support, relaxation, and religion.
Related Traits
Anxiety
Definition
Type I Anxiety includes the following categories: generalized anxiety disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, panic disorder, post-traumatic stress disorder, and social phobia.
Related Traits
Heart disease
Definition
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) or Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is a significant health risk (causing illness and death) and generally occurs when blood vessels supplying the heart with blood become damaged from cholesterol buildup & inflammation.
Related Traits
Depression
Definition
Major depression is a mood disorder that causes a persistent feeling of sadness and loss of interest.
Related Traits
Identity integration or consolidation
Definition
A persons identity refers to a self-structure: an internal, self-constructed, dynamic organization of drives, abilities, beliefs, and individual history (Marcia, 1980). Identity integration and consolidation are processes of reconciling various roles, responsibilities, and contexts to construct a coherent identity.
Related Traits
Spiritual Concerns
Definition
Spiritual concern refers to an individuals interest in the nature of social constructs labeled spiritual, religious, peak, mystical, transpersonal, transcendent, or numinous.
Related Traits
Subjective well-being
Definition
Subjective Well-Being is a construct that reflects an individuals overall evaluation on the quality or their life from their own perspective.
Related Traits
Majority-culture identification (for minorities)
Definition
Cultural identification refers to an individuals sense of belonging to a certain cultural group (e.g., Canadian, American, or Chinese).
Related Traits
Appreciate intense music styles
Definition
Intense musical styles are characterized by distorted, loud, and aggressive attributes, common in classic rock, punk, heavy metal, and power pop genres.
Related Traits
Inspiration
Definition
Inspiration refers to the process of being mentally stimulated to do something and may involve the following characteristics: transcendence (larger than normal concerns), evocation (unwilled), and motivation (desire to make manifest) (Thrash & Elliott, 2004).
Related Traits
Identity Foreclosure
Definition
According to Marcia (1980), identity foreclosure refers to individuals who have committed to a set of occupational and ideological positions (beliefs, attitudes, values), but arrived at these positions through inheritance from external influence [rather than internal reflection]
Related Traits
Appreciate sophisticated music styles
Definition
Sophisticated musical styles feature inspiring, complex, and dynamic attributes, prevalent in classical, operatic, avant-garde, and traditional jazz genres.
Related Traits
Ethnic-culture identification (for minorities)
Definition
Cultural identification refers to an individuals sense of belonging to a certain cultural group (e.g., Canadian, American, or Chinese).
Related Traits
Substance abuse
Definition
Substance abuse refers to use of drugs or alcohol to the extent that it interferes with normal social behavior.
Related Traits
Identity Achievement
Definition
According to Marcia (1980), identity achievement is the identity status aligned with people who have experienced a decision-making period and are pursuing self-chosen occupation and ideological goals (in contrast to identity status types of foreclosure, identity diffusion, and moratorium).
Related Traits
Forgiveness
Definition
The tendency to transition ones responses toward a perceived transgression from negative into neutral or positive.
Related Traits
Existential well-being
Definition
Existential Well-Being is a construct that reflects an individuals sense of meaning, purpose, and resilience.
Related Traits
Verbal Fluency
Definition
Verbal fluency is the ability to produce correct examples from a specific category. It is a cognitive task that relies on verbal knowledge, inhibition of similar words from a different semantic category, and tracking / memory of words that have already been produced.
Related Traits
Risky behavior & longevity
Definition
Risky behavior (e.g., substance abuse, hazardous driving, unprotected sex with multiple partners, attempted suicide) increases the likelihood of negative health outcomes. Longevity refers to the length of an individuals life.
Related Traits
Appreciate contemporary music styles
Definition
Contemporary musical styles represent music with rhythmic, upbeat, and electronic attributes, found in genres such as rap, electronica, Latin, and Euro-pop.
Related Traits
Humor
Definition
The general tendency to appreciate amusement, comedy, jokes, self-referential humor, jests, wit, or sarcasm.
Related Traits
Religious beliefs and behavior
Definition
MacDonald (2000) defined Religious / Spiritual concerns as a five component construct, including: cognitive orientation (perceptions and attitudes toward religious experience); experiential (mystical, transcendental, and transpersonal experiences); existential well-being (a sense of meaning, purpose, and resilience regarding ones existence); and religiousness (religious practice).
Related Traits
Gratitude
Definition
Gratitude is a general tendency to recognize and respond with grateful emotion when experiencing positive outcomes that are attributable to the benevolence of others.
Related Traits
Interpersonal Outcomes
Interpersonal outcomes are those that impact the closest relationships of a person, such as with friends and family members.
Abuse of romantic partner
Definition
Romantic abuse refers to physical acts of abuse between romantic partners (e.g., slapping, hitting, forcing sex, etc.).
Related Traits
Attractiveness
Definition
Attractiveness is the quality of being appealing and arouse interest from others.
Related Traits
Dating variety
Definition
Dating variety refers to the number of different people dated (going out on a social or romantic engagement with someone) over a period of time.
Related Traits
Family satisfaction
Definition
Family satisfaction in this context refers to quality of dyadic relationships between intergenerational family members (e.g., parent-child).
Related Traits
Peers acceptance and friendship
Definition
Peer acceptance refers to relationships within a peer group network where one peer positively acknowledges another (e.g., nominates another person as a friend).
Related Traits
Peer status
Definition
Peer status refers to relationships within a peer group network using measures such as peer acceptance (one peer nominates another as a friend) and friendship (two peers nominate each other as friends). Status often refers to differences in prominence, respect, and influence among members of a group.
Related Traits
Peer Status
Definition
Peer status refers to relationships within a peer group network using measures such as peer acceptance (one peer nominates another as a friend) and friendship (two peers nominate each other as friends). Status often refers to differences in prominence, respect, and influence among members of a group.
Related Traits
Relationship quality
Definition
Relationship quality is the overall health of a relationship, shaped by how well partners communicate, handle conflict, support each other, stay stable over time, and feel satisfied.
Related Traits
Romantic conflict
Definition
Romantic conflict refers to sources of disagreement between romantic partners.
Related Traits
Romantic dissolution
Definition
The breakup of a romantic relationship (e.g., separation or divorce).
Related Traits
Romantic satisfaction
Definition
Romantic satisfaction refers to married partners evaluations of the romantic relationship.
Related Traits
Romantic satisfaction while pursuing a romantic relationship
Definition
Romantic satisfaction refers to dating partners evaluations of the romantic relationship.
Related Traits
Social-Institutional Outcomes
Social-Institutional outcomes refer to an individual's impact to larger institutions and society in general. This includes criminal behavior, career outcomes, and citizenship.
Job attainment
Definition
Occupational attainment is a construct representing different levels of success according to an objective (e.g., low-level unskilled jobs or high-level highly skilled jobs).
Related Traits
Adhere to Shelter in Place Policy
Definition
In the context of a pandemic health crisis, sheltering in place refers to the act of adhering to publich health guidelines to stay at a primary residence, avoiding travel and other public settings as much as possible.
Related Traits
Vaccine hesitant
Definition
Vaccine hesitancy and resistance refers to a situation where someone is unsure of or against vaccination.
Related Traits
Artistic occupational interests
Definition
According to Hollands RIASEC model, artistic occupational interests which include activities involving literature, music, and art (Holland, 1996).
Related Traits
Job satisfaction
Definition
Job satisfaction refers to a pleasurable or positive emotional state resulting from the appraisal of ones job / work experiences.
Related Traits
Conservatism
Definition
Conservatism is generally associated with the values of freedom [over equality], security, power, achievement, conformity, and tradition.
Related Traits
Intrinsic success
Definition
Intrinsic success is measured in terms of an individuals job satisfaction regarding multiple facets of their career (e.g., income, supervision, job security, coworkers).
Related Traits
Volunteerism
Definition
Volunteerism involves planned prosocial behavior benefitting strangers.
Related Traits
Right-wing authoritarianism
Definition
Right-wing authoritarianism encapsulates behavior that is submissive to authorities, authoritarian aggression, and conventionalism. It is thought that this behavior may manifest as aggression towards outgroups.
Related Traits
Social occupational interests
Definition
According to Hollands RIASEC model, Social occupational interests include helping, teaching, treating, counseling, or serving others through personal interaction (Holland, 1996).
Related Traits
Occupational commitment
Definition
The psychological and emotional attachment an individual feels to an occupation.
Related Traits
Extrinsic success
Definition
Extrinsic career success (e.g., salary and promotions) refer to observable rewards from the job.
Related Traits
Financial security
Definition
Financial security refers to the degree that people perceive that their earnings are adequate for their needs.
Related Traits
Enterprising occupational interests
Definition
According to Hollands RIASEC model, Social occupational interests include persuading, manipulating, or directing others (Holland, 1996).
Related Traits
Leadership
Definition
Leadership behavior involves inspiring the support of followers to cooperate and take action.
Related Traits
Occupational performance
Definition
Occupational performance refers to employee actions and behaviors that are relevant to an organizations goals and are measurable. Measures include proficiency such as performance ratings and productivity.
Related Traits
Wear a mask as preventative health measure
Definition
Masking refers to the practice of wearing a face covering when in the presence of other people, as a method to prevent the spread of airborne diseases.
Related Traits
Criminal behavior
Definition
Criminal behavior indicates that someone has participated in an unlawful act (e.g., theft, vandalism, robbery, assault, public endangerment, etc.).
Related Traits
Investigative occupational interests
Definition
According to Hollands RIASEC model, Investigative occupational interests include activities involving exploration, understanding and prediction or control of natural and social phenomena (Holland, 1996).
Related Traits
Antisocial behavior
Definition
Antisocial behavior refers to actions that are deemed delinquent, deviant, against social norms, and violate the rights of others.
Related Traits
Explore Outcomes Further
Five Factor Simulator
Select various trait levels and visualize the impact to life outcomes
Try SimulatorResearch Article
"Indelible Implications of Individuality: Connections Between Personality Traits and Over 40 Important Life Outcomes"
Read Article